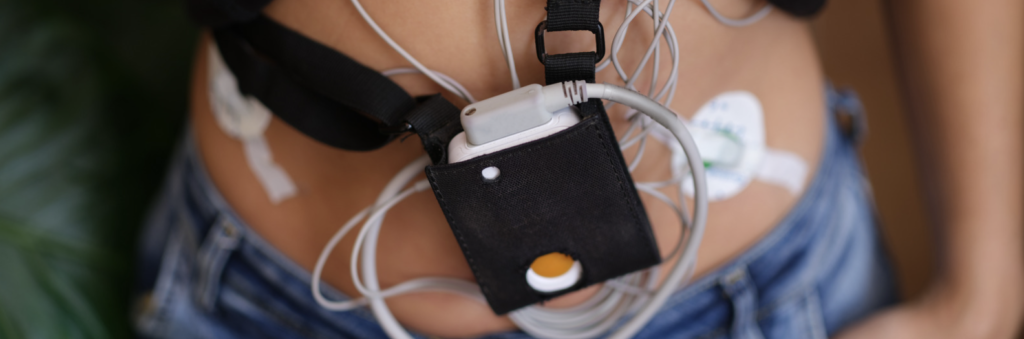
REMOTE MONITORING DEVICES: ENHANCING CHRONIC DISEASE MANAGEMENT
Chronic diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease, have become increasingly prevalent worldwide, posing significant challenges to healthcare systems and patients alike. Managing these conditions often requires continuous monitoring and frequent healthcare interactions, placing a burden on both patients and providers. However, with advancements in technology, remote monitoring devices have emerged as a powerful tool in enhancing chronic disease management. In this article, we will explore the role of remote monitoring devices, their benefits, and their impact on improving the lives of those with chronic conditions.
The Challenge of Chronic Disease Management
Chronic diseases are characterized by their long-lasting nature and the need for ongoing care. They often require regular monitoring of vital signs, medication adherence, lifestyle modifications, and frequent follow-up appointments with healthcare providers. This can be particularly burdensome for patients, leading to reduced quality of life, increased healthcare costs, and sometimes suboptimal disease control.
Enter Remote Monitoring Devices
Remote monitoring devices are a category of healthcare technology designed to bridge the gap between healthcare providers and patients, especially those with chronic conditions. These devices enable the continuous collection of vital health data, which is then transmitted to healthcare professionals for real-time assessment and intervention when necessary. Some common examples of remote monitoring devices include:
Wearable Fitness Trackers: These devices, such as smartwatches, can monitor heart rate, physical activity, sleep patterns, and sometimes even blood pressure. They provide users with insights into their daily health and fitness.
Blood Glucose Monitors: Essential for individuals with diabetes, these devices allow patients to measure their blood sugar levels at home. The data can be shared with healthcare providers for medication adjustments and lifestyle recommendations.
Blood Pressure Monitors: Patients with hypertension can track their blood pressure at home using electronic blood pressure monitors. This data assists in medication management and reduces the need for frequent clinic visits.
Remote Cardiac Monitoring Devices: These devices are used to monitor patients with heart conditions like arrhythmias. They provide real-time data on heart rhythm, allowing timely interventions.
Spirometers: For individuals with respiratory conditions like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), spirometers measure lung function and can help in disease management.
Medication Adherence Devices: Some devices can remind patients to take their medications and provide data on adherence to healthcare providers.
Benefits of Remote Monitoring Devices
The adoption of remote monitoring devices in chronic disease management offers a wide array of benefits:
Timely Intervention: Remote monitoring allows healthcare providers to detect health issues early, leading to prompt interventions and improved disease control.
Reduced Hospitalizations: By closely monitoring vital signs and symptoms, remote devices can help prevent exacerbations and hospital admissions.
Enhanced Patient Engagement: Patients become active participants in their care, leading to better adherence to treatment plans and healthier lifestyle choices.
Convenience: Patients can monitor their health from the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for frequent clinic visits and associated travel.
Data-Driven Care: Healthcare providers can make informed decisions based on real-time data, leading to more personalized and effective care.
Improved Quality of Life: Effective management of chronic diseases can lead to symptom relief and an improved quality of life for patients.
Challenges and Considerations
While remote monitoring devices offer substantial advantages, there are also challenges and considerations to address:
Data Security and Privacy: The transmission and storage of sensitive health data must comply with stringent privacy and security regulations.
Device Accuracy: The accuracy and reliability of remote monitoring devices are critical. Device malfunctions or inaccuracies can lead to incorrect clinical decisions.
Patient Training: Patients need proper training on how to use these devices effectively to ensure accurate data collection.
Health Inequities: Access to remote monitoring devices may not be equitable, potentially leaving some patients without the benefits of this technology.
Remote monitoring devices are transforming the landscape of chronic disease management by providing a means for patients and healthcare providers to collaborate effectively in real time. These devices empower patients to take control of their health, reduce the burden of frequent clinic visits, and ultimately improve their overall well-being. As technology continues to advance, the integration of remote monitoring devices into healthcare systems will likely play a pivotal role in enhancing chronic disease management, reducing healthcare costs, and ultimately improving patient outcomes.
